EARN2TRADE 50%0FF TOP ONE TRADER 45%OFF APEX 50%OFF BULENOX 91%OFF IJAN-25I

Effective Trading Strategies Setups & Journal Examples!
Effective Trading Strategies Setups & Journal Examples!
Effective Trading Strategies
Setups & Journal Examples!
Learn powerful trading strategies, proven setups, and trading journal examples to improve your performance in futures trading. Build discipline, track progress, and succeed!
Learn powerful trading strategies, proven setups, and trading journal examples to improve your performance in futures trading. Build discipline, track progress, and succeed!
Get Your Free Technical Playbook!
Get Your Free Technical Playbook!
Proven Trading Strategies
Proven Trading Strategies


Scalping Strategy
Scalping Strategy
Scalping is a fast-paced strategy where traders seek to profit from small price movements. Scalpers enter and exit positions within minutes, aiming to capture tiny price fluctuations in high volume.
How It Works:
Timeframe: 1-5 minute charts
Indicators: Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
Example Setup: Look for price crossing above VWAP on increased volume, then enter a long position. Exit as soon as the price hits a predetermined profit target.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Low risk per trade, frequent opportunities.
Cons: Requires quick decision-making, higher transaction costs.
Scalping is a fast-paced strategy where traders seek to profit from small price movements. Scalpers enter and exit positions within minutes, aiming to capture tiny price fluctuations in high volume.
How It Works:
Timeframe: 1-5 minute charts
Indicators: Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
Example Setup: Look for price crossing above VWAP on increased volume, then enter a long position. Exit as soon as the price hits a predetermined profit target.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Low risk per trade, frequent opportunities.
Cons: Requires quick decision-making, higher transaction costs.


Swing Trading Strategy
Swing Trading Strategy
Swing trading involves holding positions over days to weeks to capture medium-term market “swings.” This strategy is suitable for traders who can’t monitor the market constantly.
How It Works:
Timeframe: Daily or 4-hour charts
Indicators: Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands
Example Setup: Look for an RSI above 70 (overbought) and price touching the upper Bollinger Band for a potential short. Enter a position and hold until the RSI returns to 50.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Less time-intensive, more substantial profit potential per trade.
Cons: Requires patience, trades are exposed to overnight risks.
Swing trading involves holding positions over days to weeks to capture medium-term market “swings.” This strategy is suitable for traders who can’t monitor the market constantly.
How It Works:
Timeframe: Daily or 4-hour charts
Indicators: Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands
Example Setup: Look for an RSI above 70 (overbought) and price touching the upper Bollinger Band for a potential short. Enter a position and hold until the RSI returns to 50.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Less time-intensive, more substantial profit potential per trade.
Cons: Requires patience, trades are exposed to overnight risks.


Breakout Strategy
Breakout Strategy
The breakout strategy capitalizes on prices breaking through critical levels of support or resistance. Traders enter positions when the price “breaks out” beyond a range.
How It Works:
Timeframe: Any timeframe (depending on trading style)
Indicators: Moving Averages, Volume
Example Setup: Identify a strong resistance level. When the price breaks above on high volume, enter a long position and hold until a new resistance level is reached.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Captures high momentum moves, clear entry signals.
Cons: False breakouts can lead to losses.
The breakout strategy capitalizes on prices breaking through critical levels of support or resistance. Traders enter positions when the price “breaks out” beyond a range.
How It Works:
Timeframe: Any timeframe (depending on trading style)
Indicators: Moving Averages, Volume
Example Setup: Identify a strong resistance level. When the price breaks above on high volume, enter a long position and hold until a new resistance level is reached.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Captures high momentum moves, clear entry signals.
Cons: False breakouts can lead to losses.
The breakout strategy capitalizes on prices breaking through critical levels of support or resistance. Traders enter positions when the price “breaks out” beyond a range.
How It Works:
Timeframe: Any timeframe (depending on trading style)
Indicators: Moving Averages, Volume
Example Setup: Identify a strong resistance level. When the price breaks above on high volume, enter a long position and hold until a new resistance level is reached.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Captures high momentum moves, clear entry signals.
Cons: False breakouts can lead to losses.



Trend Following Strategy
Trend Following Strategy
Trend following is a strategy where traders look to profit from sustained price movements in one direction, either up or down. This strategy works well in trending markets and helps traders avoid counter-trend trades.
How It Works:
Timeframe: 1-hour or daily charts (depending on trend duration)
Indicators: Moving Averages (e.g., 50-day and 200-day), Average Directional Index (ADX)
Example Setup: Identify the trend using the 50-day and 200-day Moving Averages. A long trade setup would occur when the 50-day Moving Average crosses above the 200-day Moving Average (golden cross), with ADX above 20 to confirm trend strength. Enter long and hold as long as the trend remains intact.
Trend following is a strategy where traders look to profit from sustained price movements in one direction, either up or down. This strategy works well in trending markets and helps traders avoid counter-trend trades.
How It Works:
Timeframe: 1-hour or daily charts (depending on trend duration)
Indicators: Moving Averages (e.g., 50-day and 200-day), Average Directional Index (ADX)
Example Setup: Identify the trend using the 50-day and 200-day Moving Averages. A long trade setup would occur when the 50-day Moving Average crosses above the 200-day Moving Average (golden cross), with ADX above 20 to confirm trend strength. Enter long and hold as long as the trend remains intact.
Effective Trading Setups
Effective Trading Setups


Moving Average Crossover Setup
Moving Average Crossover Setup
The moving average crossover is a straightforward setup that signals when a short-term moving average crosses above or below a long-term moving average.
Example Setup:
Indicators: 50-day and 200-day Moving Averages
Long Entry: Enter a long position when the 50-day MA crosses above the 200-day MA (Golden Cross).
Short Entry: Enter a short position when the 50-day MA crosses below the 200-day MA (Death Cross).
Explanation:
The crossover signals a shift in momentum. A Golden Cross indicates a potential uptrend, while a Death Cross suggests a downtrend.
The moving average crossover is a straightforward setup that signals when
a short-term moving average crosses
above or below a long-term moving average.
Example Setup:
Indicators: 50-day and 200-day
Moving AveragesLong Entry: Enter a long position
when the 50-day MA crosses above
the 200-day MA (Golden Cross).Short Entry: Enter a short position
when the 50-day MA crosses below
the 200-day MA (Death Cross).
Explanation:
The crossover signals a shift in momentum.
A Golden Cross indicates a potential uptrend, while a Death Cross suggests a downtrend.
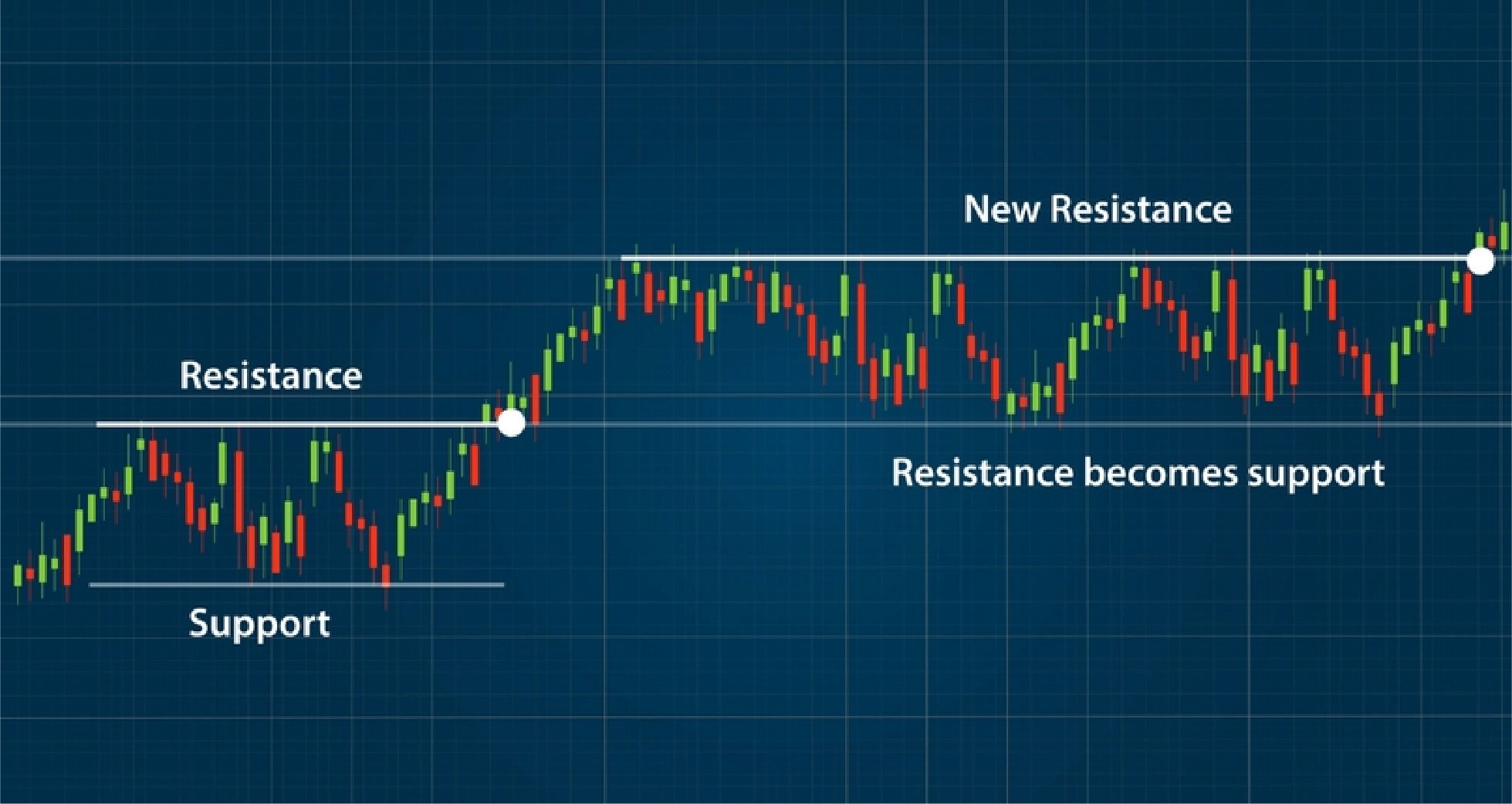


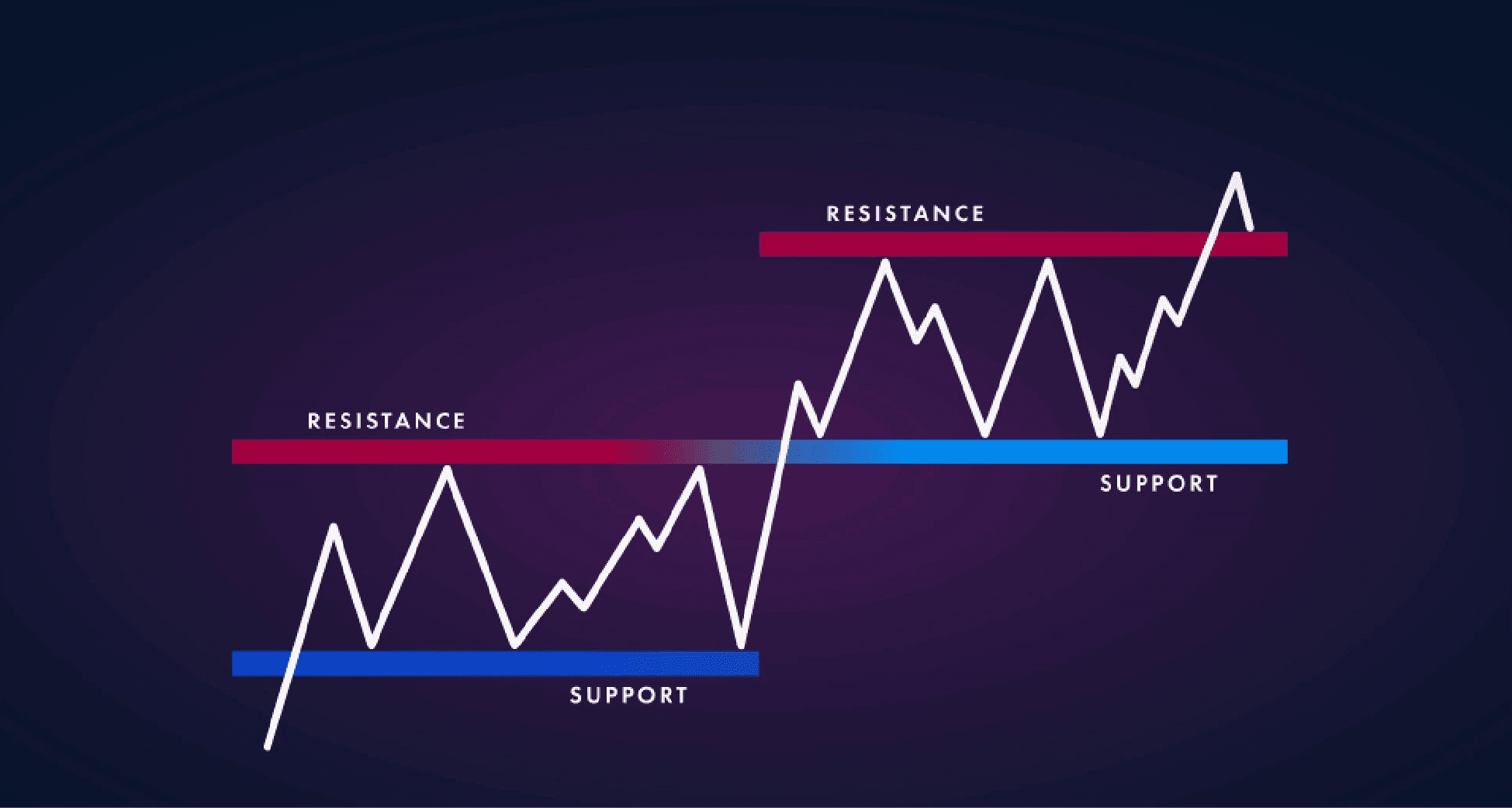
Support and Resistance Setup
Support and Resistance Setup
Support and resistance setups involve identifying key price levels where buying or selling pressures have previously reversed price direction.
Example Setup:
Indicators: Horizontal lines marking support and resistance levels.
Buy Signal: When the price touches a support level, enter a long position.
Sell Signal: When the price hits a resistance level, enter a short position.
Explanation:
Support and resistance levels act as psychological price barriers where traders often take profits or buy back into the market.
Swing trading involves holding positions over days to weeks to capture medium-term market “swings.” This strategy is suitable for traders who can’t monitor the market constantly.
How It Works:
Timeframe: Daily or 4-hour charts
Indicators: Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands
Example Setup: Look for an RSI above 70 (overbought) and price touching the upper Bollinger Band for a potential short. Enter a position and hold until the RSI returns to 50.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Less time-intensive, more
substantial profit potential per trade.Cons: Requires patience, trades
are exposed to overnight risks.
Trading Journal Examples!
Trading Journal Examples!
Keeping a trading journal helps you track, analyze, and improve your trades. Here’s an example layout for creating an effective trading journal.
Keeping a trading journal helps you track, analyze, and improve your trades. Here’s an example layout for creating an effective trading journal.
Keeping a trading journal helps you track, analyze, and improve your trades. Here’s an example layout for creating an effective trading journal.
Journal Structure
Journal Structure
Trade Details
Trade Details
Date: Enter the trade date.
Asset: Name of the asset
(e.g., E-mini S&P 500 futures).
Trade Direction: Long/Short.
Entry and Exit Price:
Record exact entry and exit.
Date: Enter the trade date.
Asset: Name of the asset
(e.g., E-mini S&P 500 futures).
Trade Direction: Long/Short.
Entry and Exit Price:
Record exact entry and exit.
Date: Enter the trade date.
Asset: Name of the asset
(e.g., E-mini S&P 500 futures).
Trade Direction: Long/Short.
Entry and Exit Price:
Record exact entry and exit.
Date: Enter the trade date.
Asset: Name of the asset
(e.g., E-mini S&P 500 futures).
Trade Direction: Long/Short.
Entry and Exit Price:
Record exact entry and exit.
Strategy Used
Strategy Used
Describe the strategy
(e.g., Moving Average Crossover, Support & Resistance).
Note the setup (e.g., price above/below support, volume increase).
Describe the strategy
(e.g., Moving Average Crossover, Support & Resistance).
Note the setup (e.g., price above/below support, volume increase).
Describe the strategy (e.g., Moving Average Crossover Support & Resistance).
Note the setup (e.g., price above/below support,
volume increase).
Describe the strategy
(e.g., Moving Average Crossover,
Support & Resistance).
Note the setup (e.g., price
above/below support, volume increase).
Trade Outcome
Trade Outcome
Profit/Loss: Calculate and record the P/L of the trade.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Note the initial risk-to-reward ratio.
Profit/Loss: Calculate and record the P/L of the trade.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Note the initial risk-to-reward ratio.
Profit/Loss: Calculate and
record the P/L of the trade.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Note the initial risk-to-reward ratio.
Profit/Loss:
Calculate and record
the P/L of the trade.
Risk-Reward Ratio:
Note the initial risk-to-reward ratio.
Analysis
Analysis
Lessons Learned: What worked or didn’t work in this trade?
Emotions/Thoughts: Note any emotions (e.g., nervous, overconfident) and how they affected decisions.
Lessons Learned: What worked
or didn’t work in this trade?
Emotions/Thoughts: Note any emotions (e.g., nervous, overconfident) and how they affected decisions.
Lessons Learned: What worked or didn’t work in this trade?
Emotions/Thoughts: Note any emotions (e.g., nervous, overconfident) and how they affected decisions.
Lessons Learned:
What worked or didn’t work in this trade?
Emotions/Thoughts:
Note any emotions (e.g., nervous, overconfident) and how they affected decisions.
